Have trouble keeping your projects on track in the face of constant change and tight deadlines?
Did you know that organizations that invest in proven project management practices can save up to 28 times more 1 than those that do not? 💸
In a nutshell, project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, and managing resources to achieve specific project goals and objectives while increasing efficiency, encouraging growth, and delivering high-quality results.
This project management guideline will give you a thorough understanding of essential principles, methodologies, and best practices.
Without further ado, let us start!
Why Is Project Management Crucial?
Quick Overview
| Common Pain | How PM Resolves It | The Impact |
| Inefficient Resource Utilization | Streamlining processes and optimizing resource allocation | 89% of high-performing organizations use project management practices to enhance efficiency |
| Lack of Clear Goals and Objectives | Setting clear goals and objectives aligned with the strategic vision | Organizations with mature project management practices meet their goals 2.5 times more often |
| Low Productivity | Improving coordination and workflow through structured planning and execution | Organizations with mature project management practices have 38% more projects meeting original goals |
| Poor Quality Deliverables | Implementing rigorous planning, quality control measures, and continuous monitoring | 77% of high-performing projects meet quality standards compared to 56% of low performers |
| Ineffective Communication | Establishing clear communication channels for all team members and stakeholders | Effective communication decreases project failure rates by 17% |
| Difficulty Adapting to Changes | Using flexible methodologies like Agile to respond quickly to changing requirements | 87% of companies using Agile practices manage change more effectively |
| Disorganization and Missed Deadlines | Utilizing project management tools like Gantt charts and Kanban boards to track progress and manage tasks | 79% of organizations using project management software report better project organization |
- Efficiency: How does project management allocate resources? By streamlining processes and eliminating waste, project managers can ensure that their time, money, and effort are well spent.
Wellingtone’s study 2 found that 89% of high-performing organizations use project management to increase efficiency.
- Growth and Development: PM also helps set clear goals and objectives that align with your strategic vision.
According to PMI, organizations with mature project management practices meet their goals 2.5 times more often3 and waste 13 times less money than their counterparts.
- Increased Output: Project Management enables organizations and individuals to deliver more using the same amount of resources and time. That is facilitated by improving coordination and workflow, structured planning and execution, reducing downtime, and enhancing task efficiency.
A study by PMI4 indicates that organizations with mature project management practices have 38% more completed projects.
- Quality Deliverables: PM provides rigorous planning, quality control measures, and continuous monitoring to always check the quality box.
Research shows that 77% of companies 5 with a project management strategy meet quality standards and stakeholder expectations, compared to 56% of low performers.
- Clear Communication: PM sets clear channels to always keep your team and stakeholders informed and aligned. This is crucial as effective communication raises the chances of project failure.
- Flexibility: PM helps you adapt to changes with flexible methodologies like Agile, allowing for quick responses to changes and unforeseen challenges.
- Organization: Project management tools like Gantt charts and Kanban boards track progress, assign tasks, and manage deadlines.

Benefits of Project Management For Your Business
| Benefit | Description |
| Save Time and Money | – Systematic planning and execution minimize delays and avoid costly mistakes.- Clear timelines and budgets ensure efficient use of resources. |
| Improve Internal Communications | – Structured communication plans keep all team members and stakeholders aligned.- Regular updates and clear reporting channels reduce misunderstandings and foster collaboration. |
| Make Better Business Decisions | – Data-driven insights and performance metrics guide informed decision-making.- Strategic approaches improve resource allocation, risk management, and task prioritization. |
| Iterate on Your Successes | – Continuous improvement through analyzing completed projects.- Identifying best practices and learning from past mistakes enhance future performance. |
| Enhance Quality | – Consistent adherence to quality standards through structured processes.- Rigorous planning, monitoring, and control ensure high-quality deliverables. |
| Boost Team Morale | – Clear goals, well-defined roles, and effective communication motivate and engage the team.- Understanding contributions and seeing tangible progress increase morale and productivity. |
| Mitigate Risks | – Proactive risk management identifies potential risks early.- Developing mitigation strategies ensures smoother project execution. |
| Achieve Strategic Alignment | – Projects align with organizational goals and strategic objectives.- Contributes to achieving broader business goals and delivering stakeholder value. |
Read More: 20 Benefits of Project Management ✅ +92% Success Rate Formula
Fundamentals of Project Management
Several key principles underpin effective project management to get every project to meet its objectives on time. Here’s a concise overview of these fundamental principles:
Scope Management
- Define boundaries to keep projects on track
- Determine all work required and avoid scope creep
- Align stakeholders’ expectations with project delivery
Read More: How To Define Boundaries In a Project
Time Management
- Create detailed schedules that include tasks, milestones, and deadlines
- Ensure progress is as planned, and address any delays immediately
- Use tools like Gantt charts to visualize timelines and keep everyone on track
▶️ Effective time management is crucial for project success, and understanding lead time plays a significant role in this process. For a comprehensive breakdown of lead time, including its definition, calculation, and strategies for reduction, check out our detailed guide on What Is Lead Time?.
Cost Management
- Budgeting and financial management to avoid overspending
- Include cost estimation, budgetary planning, and cost control
- Keep track of your expenses to make informed decisions and stay financially healthy
Quality Management
- Set quality objectives and carry out quality assurance activities
- Implement quality control measures to ensure that the required standards are met
- Ensure that the deliverables satisfy the stakeholders
To discover how to achieve superior project outcomes and minimize costly errors, check out our comprehensive guide on Project Quality Management.
Risk Management
- Identify potential risks and assess their impact
- Create and implement mitigating strategies
- Anticipate issues to avoid possible disruptions
Stakeholder Management
- Engage stakeholders and respond to their needs and expectations
- Identify stakeholders, learn about their interests, and maintain regular communication
- Develop strong relationships to encourage support and collaboration
Read More: Project Management Fundamentals
Overview of Major Project Management Methodologies
Waterfall
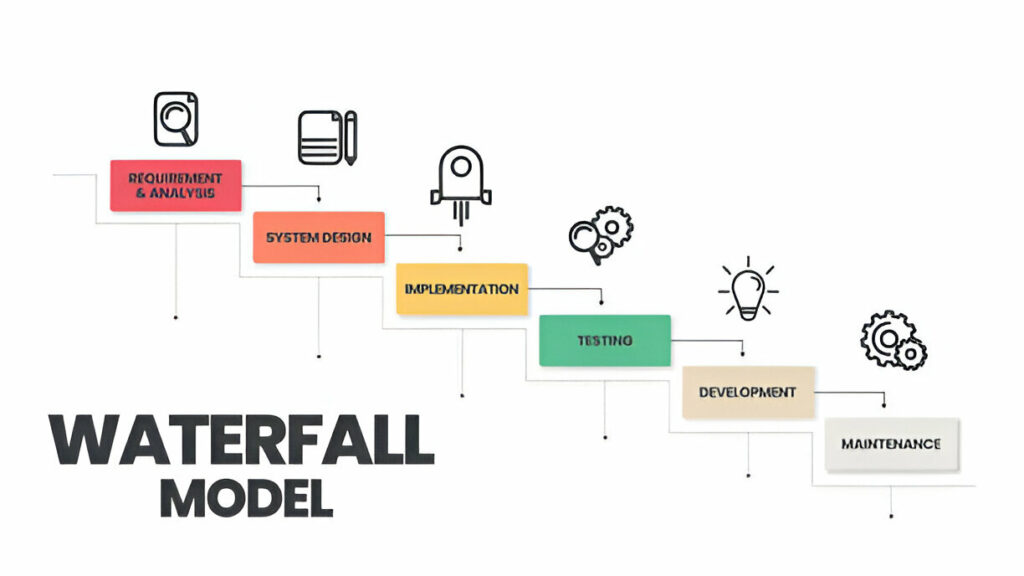
Waterfall Project Management is a traditional and popular methodology distinguished by its linear and sequential approach. Here’s a quick overview of its main components:
Linear structure
- Follows a strict sequence, with each phase depending on the deliverables of the previous one
- The phases include requirement gathering, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance.
- Clear progression for more efficient task and time management.
Detailed planning
- This includes defining project requirements, creating documentation, and developing a schedule.
- Upfront planning to ensure that all stakeholders understand the scope and objectives.
- According to PMI 6, around 59% of traditional organizations use a waterfall approach.
Defined Phases
- Each phase includes specific deliverables and review procedures.
- For example, the design phase must be reviewed and approved before proceeding to implementation.
- The stage-gate process ensures quality and identifies problems early on.
Easy to Manage
- The structured approach simplifies management, particularly for projects with clear requirements.
- Clear, sequential steps and detailed documentation make it easier to track progress and identify potential bottlenecks early on.
Challenges
- Inflexibility in adapting to changes, which can be costly and difficult to implement late.
Studies 7 have shown that Agile projects are twice as successful as Waterfall projects, highlighting the challenges of working in dynamic environments.
Agile
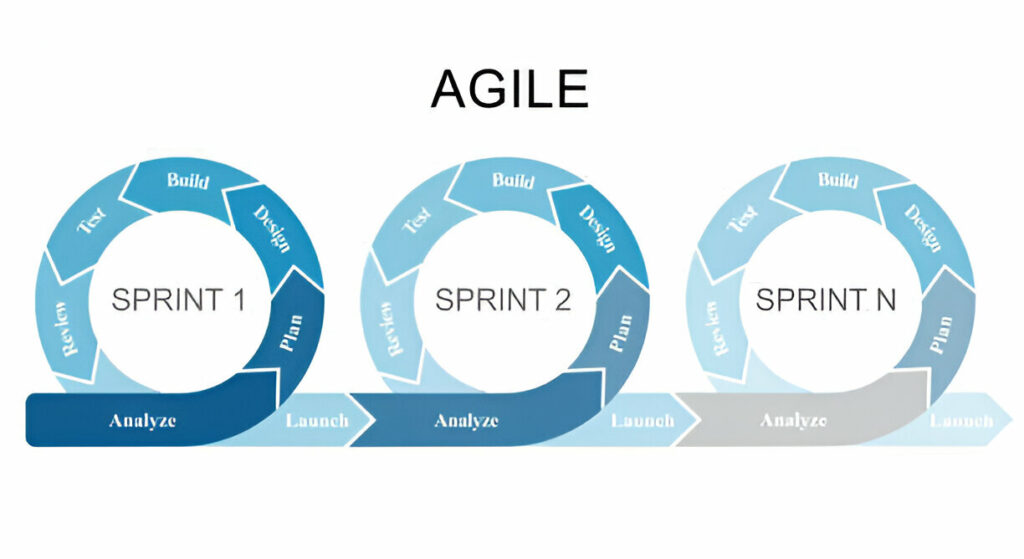
Agile Project Management is a dynamic and adaptable approach to managing complex and constantly changing project requirements. Here’s a brief overview of the Agile methodology and its main components:
Iterative Process
- Agile divides projects into smaller, manageable units known as sprints.
- Each sprint lasts two to four weeks and produces a usable product increment.
- Regular feedback and adjustments ensure that the project evolves based on stakeholder feedback.
Flexibility and Adaptability
- Agile is perfectly flexible and adaptable to changing requirements and unexpected challenges.
- Ideal for fast-paced industries, such as software development.
- 87% of organizations 8 that use Agile practices improve their ability to manage change.
Collaboration and Communication
- Encourages ongoing collaboration among team members and stakeholders.
- Regular meetings (daily stand-ups, sprint reviews) keep everyone in sync.
- Promotes teamwork and improves project outcomes.
Customer-Centric Approach
- Agile focuses on providing value to customers.
- Engages stakeholders throughout the project and prioritizes their feedback.
- Agile projects perform +28% better 9 in meeting customer expectations.
Incremental Delivery
- Agile promotes early and frequent releases of project components.
- Provides value to customers sooner and identifies problems early.
- 71% of businesses report faster time-to-market for Agile projects.
In summary, Agile is best suited for projects where requirements are likely to change and flexibility is essential.
#1 choice for software development, marketing, and industries experiencing rapid change.
Challenges
- Agile needs strong collaboration and commitment from all team members.
- Improper implementation can lead to scope creep and difficulties in meeting deadlines and budgets.
Scrum

Scrum is a widely used Agile framework that enhances team collaboration and productivity. Here’s a concise overview of its key aspects:
- Framework Structure:
- Roles: Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team.
- Events: Daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives.
- Artifacts: Product backlog, sprint backlog, and increment.
- Clear responsibilities and accountability boost team dynamics.
- Daily Stand-ups:
- Short daily meetings to synchronize work.
- Discuss progress and identify obstacles.
- Ensure alignment and maintain focus on sprint goals.
- Sprint Reviews and Retrospectives:
- Sprint Review: Present product increment to stakeholders for feedback.
- Sprint Retrospective: Reflect on and improve processes.
- Crucial feedback loop for ongoing improvement.
- Backlog Management:
- The Product Owner maintains a prioritized product backlog.
- Ensures the team works on the most valuable tasks.
- Keeps the project aligned with business priorities.
- Customer Focus:
- Early and frequent delivery of value to the customer.
- Incorporate feedback at the end of each sprint.
- McKinsey reports 10 a 30% improvement in customer satisfaction with Scrum.
- Best Suited For:
- Ideal for projects with evolving requirements.
- Commonly used in software development and marketing.
Read More: Scrum Project Management ✅ Guide for +800% Productivity
Kanban

Kanban Project Management is a visual methodology that emphasizes continuous delivery without overburdening the team. Here’s an overview of its key aspects and why it appeals to project managers:
Visual Workflow Management
Kanban uses a visual board to represent the workflow, with columns indicating different stages.
Tasks are represented as cards that move from one column to the next as they progress. This visual representation helps teams see the workflow, identify bottlenecks, and improve overall efficiency.
According to Kanban University, 78% of teams using Kanban report increased workflow visibility.
Work in Progress (WIP) Limits
A fundamental principle of Kanban is limiting the amount of work in progress. By setting WIP limits, teams can focus on completing tasks before starting new ones to reduce the headache of multitasking.
Continuous Delivery
Unlike traditional methodologies that follow a strict sequence, Kanban promotes ongoing delivery. Tasks are completed and delivered as soon as they are ready, securing a steady flow of value to the customer.
Kanban is incredibly beneficial if your team needs to respond quickly to changing priorities and requirements.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Kanban is highly flexible and adaptable to various industries and project types. Its simplicity makes it easy to implement and scale, whether you’re managing a software development project, construction site, healthcare clinic, or a marketing campaign.
Improved Team Collaboration
The visual nature of Kanban boards facilitates better team collaboration and communication. Regular updates and visual signals confirm that everyone is on the same page to minimize misunderstandings.
Best Suited For: Kanban is excellent for your team to manage ongoing work with high flexibility in their workflow. It’s trendy in software development, manufacturing, and service industries where continuous value delivery and adaptability are essential.
Challenges: While Kanban offers many benefits, it also requires discipline to maintain WIP limits and manage the flow of tasks effectively.
Read More: Good Icebreaker Questions for Team Collaboration (Chosen by Experts) ✅
Lean
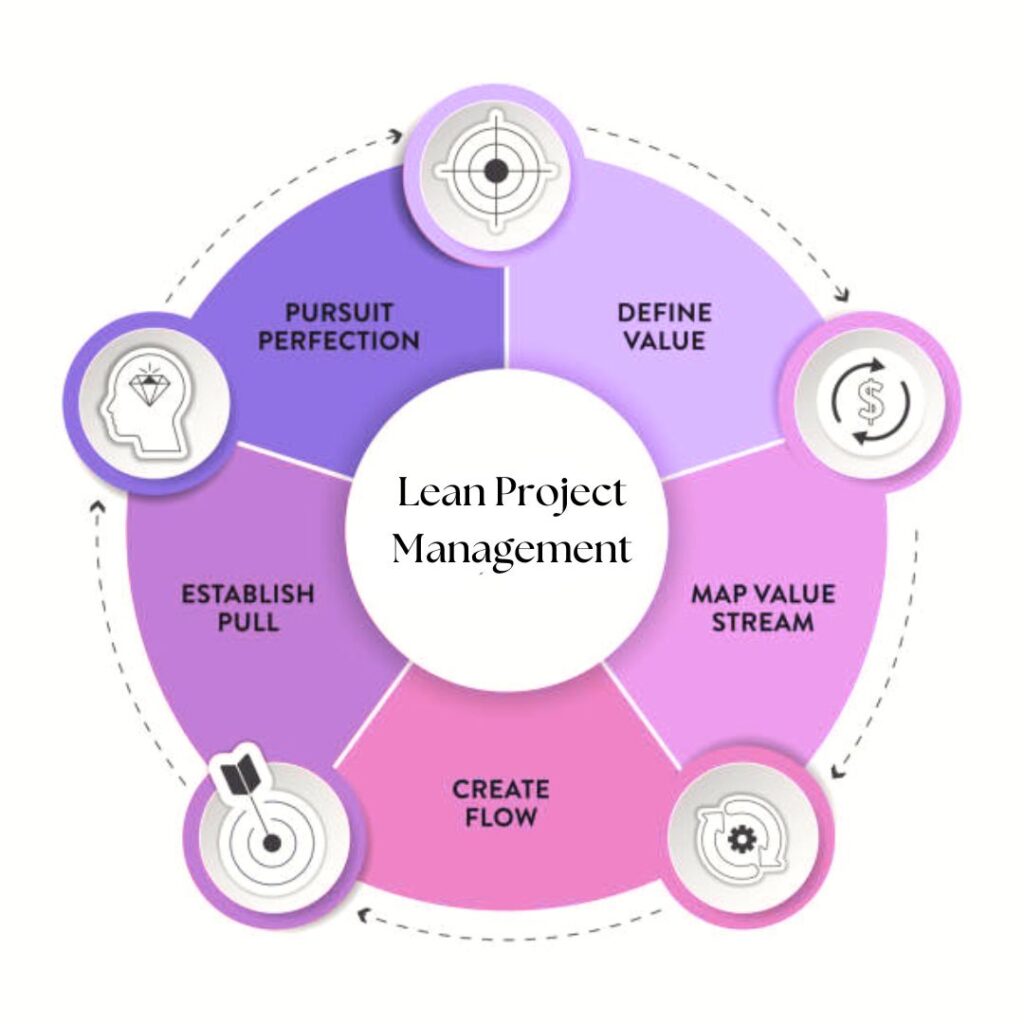
Lean project management focuses on delivering maximum value to the customer by eliminating waste and continuously improving processes. Here’s a concise overview of the key aspects and benefits of Lean:
- Value Stream Mapping:
- Identifies and maps all steps in a process to understand how value flows to the customer.
- Pinpoints and eliminates activities that do not add value to streamline operations.
- Originates from the Toyota Production System11, revolutionizing manufacturing by improving supplier and customer interactions while eliminating waste.
- Eliminating Waste:
- Systematic removal of waste (Muda) from processes.
- Includes reducing excess inventory, minimizing waiting times, and eliminating unnecessary steps.
- Focuses on value-adding activities, making teams more efficient and productive.
- McKinsey studies12 show Lean methodologies can reduce project costs by 20-30%.
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen):
- Encourages a culture of continuous improvement.
- Teams regularly assess processes and make gradual improvements.
- Leads to better quality, higher efficiency, and increased customer satisfaction.
- Research indicates companies practicing Kaizen see a 10-20% annual improvement 13in performance metrics.
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Production:
- Promotes creating products only when needed and in exact quantities required.
- Minimizes waste, reduces inventory costs and improves overall efficiency.
- Implementation can lead to a 50% reduction in inventory levels and significant cost savings.
- Empowering Teams:
- Empower employees to make decisions and take ownership of their work.
- Fosters a culture of accountability and continuous learning.
- Companies adopting Lean principles report a 30% increase in employee engagement.14
- Best Suited For:
- Particularly effective in manufacturing and production environments.
- Successfully adapted to healthcare, software development, and other service industries where efficiency and waste reduction are critical.
- Challenges:
- Requires a cultural shift and commitment to continuous improvement.
- Teams must be willing to regularly review and refine their processes to sustain improvements.
Six Sigma

Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology focused on improving processes by eliminating defects and ensuring quality. Here’s a concise overview of Six Sigma and its key aspects:
- Data-Driven Approach:
- Relies on statistical analysis for decision-making.
- Focuses on making the right decisions based on observed evidence.
- Companies using Six Sigma report significant improvements 15in process efficiency and quality.
- DMAIC Framework:
- The core of Six Sigma, a structured approach to systematically improve processes:
- Define the problem.
- Measure current performance.
- Analyze data to identify root causes.
- Improve processes by implementing solutions.
- Control the new process to ensure sustainability.
- Reduces defects and process variability.
- The core of Six Sigma, a structured approach to systematically improve processes:
- Focus on Quality:
- Aim for near-perfect quality by reducing defects to fewer than 3.4 per million opportunities.
- Ensures products and services meet the highest quality standards.
- General Electric, a pioneer in Six Sigma, reportedly saved billions of dollars 16through its implementation.
- Roles and Certification:
- Involves specific roles like Green Belts, Black Belts, and Master Black Belts with defined responsibilities and expertise levels.
- Certification is highly demanded and can significantly advance your career.
- Customer Satisfaction:
- Directly impacts customer satisfaction by focusing on quality and efficiency.
- Improved processes lead to better products, meeting or exceeding customer expectations.
- Studies 17 show that companies using Six Sigma report higher customer satisfaction rates.
- Best Suited For:
- Ideal for industries where quality and precision are critical, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and finance.
- A structured, data-driven approach makes it perfect for systematically improving processes and outcomes.
- Challenges:
- It can be resource-intensive and requires a strong commitment from the organization.
- It involves extensive training and cultural shifts, which can be challenging for some companies.
Critical Path Method
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a powerful project management technique used to identify the sequence of crucial steps that determine your project’s duration. Here’s an engaging overview of CPM and why it’s essential for project managers:
Defining the Critical Path
CPM focuses on identifying the longest sequence of tasks in a project plan that must be completed on time for the entire project to be finished by its due date.
This sequence, known as the critical path, highlights the tasks that directly impact the project’s timeline. Missing a deadline on any of these tasks will delay the entire project.
Detailed Scheduling
By breaking down the project into individual tasks, CPM gives you detailed scheduling and resource allocation. Each task is assigned a start and end date, and dependencies between tasks are clearly defined.
The result? You, as a project manager, can anticipate potential delays to allocate resources more effectively.
Visualization Tools
CPM often uses Gantt charts and network diagrams to visualize the project timeline and relationship between tasks.
Equipped with a clear and comprehensive overview of the project’s progress, you will monitor and adjust schedules as needed. Studies 18 show that visual project management tools can increase team productivity by 25-30%. 📈
Flexibility and Risk Management
While CPM highlights the critical path, it also identifies non-critical tasks with scheduling flexibility, known as float or slack.
This flexibility allows you to adjust resources and timelines for non-critical tasks — without affecting the overall project completion date.
CPM is excellent for your complex projects with many interdependent tasks, such as construction, engineering, and large-scale event planning.
Its power to provide a clear roadmap and anticipate potential bottlenecks makes it invaluable where timing is crucial.
However, you should note that any inaccuracies in the initial planning phase can lead to significant scheduling issues later on. Besides, maintaining the schedule can be resource-intensive, especially for very large projects. ⚠️
Read More: 10 Proven Hacks for Reducing the Duration of Project Management
PRINCE2
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a process-driven methodology that provides a structured framework for managing projects of any size or complexity. Here’s a concise overview of PRINCE2’s key aspects and benefits:
- Structured Approach:
- Divided into 7 processes:
- Starting Up a Project
- Initiating a Project
- Directing a Project
- Controlling a Stage
- Managing Product Delivery
- Managing a Stage Boundary
- Closing a Project
- Provides a clear roadmap covering all aspects of project management.
- Reduces the risk of overlooking critical steps and improves efficiency.
- Divided into 7 processes:
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- Clearly defines roles and responsibilities.
- Ensures all team members understand their duties.
- Improves accountability and communication among team members.
- Focus on Business Justification:
- Promotes a strong business case to keep the project viable and aligned with business objectives.
- Ensures informed decision-making and value delivery.
- 88% of PRINCE2 practitioners believe the methodology provides a clear return on investment.
- Scalability and Flexibility:
- Highly scalable to suit the specific needs of any project.
- Adaptable to various industries and project types.
- Remains relevant and effective regardless of project size or complexity.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement:
- Encourages incorporating lessons learned from previous projects into current and future ones.
- Helps refine processes and avoid past mistakes.
- Leads to more successful project outcomes.
- Best Suited For:
- Ideal for large, complex projects in government, IT, construction, and finance.
- Essential where structured processes and clear roles are crucial.
- Ensures alignment with organizational goals.
- Challenges:
- It can be resource-intensive and may require extensive training and certification.
- A structured approach might be overly rigid for smaller or more agile projects.
Quick Overview of All Project Management Methodologies
| Methodology | Pros | Cons | Best For | Key Industries | Example Use Cases |
| Waterfall | Clear structure and documentation Easy to manage and understand Defined stages and timelines | Inflexible to changes Late-stage issues can be costly Not ideal for complex, iterative projects | Projects with well-defined requirements | Construction, Manufacturing | Building a bridge, Developing a new product with fixed requirements |
| Agile | Highly flexible and adaptive Continuous customer feedback Encourages collaboration and innovation | Can be less predictable Requires high commitment and experience Potential for scope creep | Projects needing flexibility and rapid changes | Software Development, Marketing | Developing a software application, Launching a marketing campaign |
| Scrum | Focuses on quick delivery of product increments Enhances team collaboration Frequent feedback loops | Can be intense and demanding Requires disciplined adherence to roles Possible issues with scalability | Teams that thrive on rapid iterations and feedback | Software Development, Product Development | Sprint-based software development, Creating a new product feature |
| Kanban | Visualizes workflow effectively Limits work in progress for better focus Flexible and adaptable | Can be difficult to manage without clear policies May require a cultural shift for the team | Teams needing continuous delivery and visualization | IT, Service Industries | IT support and maintenance, Continuous delivery in service teams |
| Lean | Focuses on waste reduction Continuous improvement culture Enhances efficiency and quality | Can be resource-intensive to implement Requires strong leadership and commitment | Organizations aiming for efficiency and quality | Manufacturing, Healthcare | Streamlining production processes, Improving healthcare services |
| Six Sigma | Data-driven decision making High focus on quality and defect reduction Enhances process efficiency | Can be complex and rigid Requires significant training Often resource-intensive | Industries requiring high precision and quality | Manufacturing, Healthcare, Finance | Reducing defects in manufacturing, Improving patient care processes |
| PRINCE2 | Structured and process-driven Clear roles and responsibilities Scalable and flexible | Can be seen as bureaucratic Requires extensive documentation Training and certification needed | Large, complex projects needing clear processes | Government, IT, Construction | Government infrastructure projects, Large IT system implementations |
| Critical Path | Identifies critical tasks and dependencies Helps in efficient resource allocation Improves scheduling accuracy | Requires precise estimation of task durations Can be complex to manage Not flexible to changes | Projects with interdependent tasks and strict timelines | Construction, Engineering | Construction of large buildings, Engineering projects with many dependencies |
Key Phases of Project Management

Effective project management is all about navigating through 5 critical phases: Initiation, Planning, Execution, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closing.
Let’s dive into these phases and explore practical steps and best practices for each.
Phase 1: Initiation (Defining the Project)
Initiation is the first phase, measuring your project’s value and feasibility. In this phase, you define the project at a broad level. Key steps include:
- Developing a Project Charter: This document outlines the objectives, scope, purpose, and stakeholders. It acts as a reference point throughout your project lifecycle.
- Identifying Stakeholders: Determine who will be affected by the project and their needs and expectations. Engaging stakeholders early to secure their buy-in and support.
Phase 2. Planning (Outlining the Project)
Here, you set the project roadmap. This phase is crucial as it guides your team toward project goals. Key steps include:
- Setting Objectives and Scope: Clearly define the project’s goals and boundaries.
- Creating a Detailed Project Plan: This involves schedules, budgets, resource allocation, and risk management strategies.
- Developing a Communication Plan: Determine how information will be communicated to stakeholders.
Best Practice: Use project management tools like Mirorim to create detailed Kanban boards to visualize timelines and task dependencies.
Phase 3: Execution (Implementing the Plan)
Execution is where the actual work happens. This phase involves putting the project plan into action and managing the tasks. Key steps include:
- Coordinating People and Resources: Make sure your team understands their roles and responsibilities.
- Managing Stakeholder Expectations: Keep stakeholders engaged via regular updates and meetings.
- Executing Project Plans: Follow the detailed plans developed in the planning phase to handle any issues.
Best Practice: Promote genuine communication and collaboration within your team to resolve potential issues quickly.
Phase 4: Monitoring and Controlling (Tracking Progress)
This involves continuously tracking the project’s performance to make necessary adjustments. Key steps include:
- Performance Reporting: Regularly measure project performance against the initial project objectives.
- Managing Changes: Implement structured change management to handle unexpected changes in scope, schedule, or resources.
- Quality Control: Ensure that project deliverables meet the required quality standards.
Best Practice: Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and identify areas that need improvement.
Phase 5: Closing (Finalizing the Project)
Closing is the final phase of formally closing and handing over the project. Key steps include:
- Final Deliverables: Make sure all project deliverables are completed and meet the approval criteria.
- Post-Implementation Review: Review to capture lessons learned and best practices for future projects.
- Formal Closure: Complete all project documentation and get formal sign-off from stakeholders.
Best Practice: Document lessons learned and share them with your team to improve processes in future projects. You can also publicly publish a detailed report to demonstrate your project’s excellent performance.
Read More: Project Management Process ⭐ Master 5 Key Phases
Roles in Project Management

Project Manager
The Project Manager is the cornerstone of any project, responsible for planning, executing, and closing projects. They ensure that the project aligns with the company’s goals, stays within budget, and meets deadlines. Key responsibilities include:
- Defining Project Scope: Clearly outlining what the project will deliver.
- Scheduling and Planning: Creating detailed project plans and timelines.
- Resource Allocation: Ensuring the right resources are available when needed.
- Risk Management: Identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies.
- Stakeholder Communication: Keeping stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the project lifecycle.
A successful Project Manager is an effective communicator, a strategic thinker, and a problem-solver, capable of leading their team to success amidst challenges.
Project Coordinator
The Project Coordinator plays a supportive role, assisting the Project Manager in various administrative tasks to keep the project on track. Their responsibilities often include:
- Scheduling Meetings: Organizing and managing project meetings.
- Tracking Progress: Monitoring the progress of project tasks and updating project plans accordingly.
- Documentation: Maintaining project documentation, including meeting minutes, reports, and schedules.
- Facilitating Communication: Ensuring smooth communication between team members and stakeholders.
- Supporting Risk Management: Assisting in identifying risks and implementing mitigation plans.
Project Coordinators are detail-oriented, organized, and excellent multitaskers. They ensure that all the administrative aspects of the project run smoothly.
Read More: Project Coordinator vs Project Manager 💡 Must-Know Differences
Project Team Members
Project Team Members are the individuals who actually carry out the project tasks. They bring specialized skills and expertise to the table and work collaboratively to achieve the project goals. Their responsibilities include:
- Executing Tasks: Completing assigned tasks according to the project plan.
- Collaborating with Team: Working closely with other team members to ensure tasks are completed efficiently.
- Providing Input: Offering insights and feedback to improve project outcomes.
- Adhering to Deadlines: Ensuring tasks are completed on time and to the required standard.
- Reporting Progress: Regularly update the Project Manager and Coordinator on task progress.
Effective Project Team Members are skilled, proactive, and collaborative, contributing their expertise to ensure the project’s success.
Key Project Management Skills

Communication
- Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful project management.
- Involves clearly conveying information, expectations, and updates to all stakeholders.
- Helps avoid misunderstandings, fosters collaboration, and ensures everyone is on the same page.
People Skills
- Strong interpersonal skills enable building positive relationships with team members and stakeholders.
- Empathy, active listening, and the ability to inspire and motivate others.
- Crucial for creating a collaborative and productive project environment.
Problem-solving
- Frequently encounter challenges that require quick and effective solutions.
- Involves identifying issues, analyzing options, and implementing the best solutions.
- Ensures projects stay on track despite any obstacles.
Persuasion Skills
- Essential for gaining support for project initiatives and changes.
- It helps advocate for necessary resources, influence decisions, and drive project momentum.
Technical Skills
- Understanding the technical aspects of the project is vital.
- Enables comprehension of the project’s complexities, effective communication with technical team members, and informed decision-making.
Conflict Resolution
- Effective conflict resolution involves addressing disagreements constructively, mediating disputes, and finding mutually beneficial solutions.
- Maintains a harmonious and focused project team.
Business Acumen
- Aligns project goals with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Includes understanding of market trends, financial principles, and business operations.
- Helps make decisions that add value to the organization.
Time Management
- Efficient time management skills are crucial for meeting deadlines and ensuring tasks are completed on schedule.
- Involves prioritizing tasks, managing workload, and avoiding procrastination.
- Keeps the project on track and reduces stress.
Motivation Skills
- Keeps teams motivated and engaged.
- Recognizing and rewarding achievements, creating a positive work environment, and encouraging professional growth.
- Motivated team members are more productive and committed to the project’s success.
Accountability
- Holding oneself and the team accountable is essential for maintaining high standards and ensuring project success.
- Involves setting clear expectations, monitoring progress, and addressing performance issues promptly.
- Fosters a culture of responsibility and excellence.
Mirorim, The Best Project Management Tool
Among the available project management tools, Mirorim is second to none. Its unique combination of capabilities, emphasis on team performance management, and synergy set it above earlier instruments. Here are the reasons Mirorim is the best fit for your project management requirements:
| Feature | Mirorim | Comparison with Others |
| Comprehensive Task Management | Offers detailed task management capabilities, allowing teams to assign, track, and complete tasks efficiently. | Other tools like Trello and Asana offer task management but lack the depth and integration seen in Mirorim. |
| Self-Care Center | Unique self-care center where users can track their productivity and well-being, promoting a balanced work-life approach. | No comparable feature in other major PM tools, making Mirorim a pioneer in integrating self-care with productivity. |
| Cross-Platform Compatibility | Available on Android, iOS, and Desktop, ensuring seamless access and synchronization across devices. | While many tools offer cross-platform compatibility, Mirorim excels in its seamless and intuitive user experience. |
| Anonymous Performance Rating | Enables anonymous feedback on team performance, fostering honest and constructive evaluations. | Most tools lack this feature, providing a unique advantage in maintaining transparency and accountability. |
| User-Friendly Interface | Intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface designed to minimize the learning curve and enhance user experience. | Other tools like Microsoft Project are powerful but often criticized for their steep learning curves. |
| Affordable Pricing | Positioned as an affordable solution without compromising on features and quality. | Many top-tier tools come with high subscription costs, whereas Mirorim offers competitive pricing without hidden fees. |
| Enhanced Collaboration Tools | Includes real-time collaboration features, such as chat, file sharing, and collaborative document editing, to streamline teamwork. | Similar features are available in tools like ClickUp and Monday.com, but Mirorim integrates them more seamlessly. |
| Robust Security Measures | Implements advanced security protocols to protect project data, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. | While tools like Jira offer strong security, Mirorim’s comprehensive measures set a new standard for data protection. |
Why Choose Mirorim?
- Innovative Features: Mirorim’s self-care center is built to multiply your team synergy, setting it apart from competitors.
Mirorim is designed with you in mind. The intuitive interface and cross-platform compatibility make it accessible and comfortable for all your team members.
- Cost-Effective: Mirorim offers a robust set of features at an affordable price, making it the best value in project management tools.
- Enhanced Collaboration: With real-time collaboration and performance management features, Mirorim makes teamwork as delightful as quality time with your close friends.
- Unmatched Security: Advanced security measures and super-advanced encryption methods protect your team’s invaluable data, giving you peace of mind.
Project Management Real-World Examples
1. Construction Industry: Building a Skyscraper
- Methodology: Waterfall
- Results: Completed 2 months ahead of schedule, reducing costs by 10%.
- Key Highlights: The project adhered strictly to the Waterfall methodology, ensuring that each phase was meticulously planned and executed before proceeding to the next. Detailed Gantt charts allowed for precise tracking of tasks and timelines, contributing to the project’s early completion and cost savings.
- Lessons Learned: A major challenge was coordinating multiple contractors to align them with the project schedule. Regular meetings and a centralized project management tool helped maintain synchronization and resolve conflicts swiftly.
2. Healthcare: Implementing an Electronic Health Record (EHR) System
- Methodology: Agile
- Results: Improved patient data accessibility by 35% and reduced record retrieval time by 50%.19
- Key Highlights: Agile methodology facilitated iterative development and regular stakeholder feedback, ensuring the EHR system met the users’ needs. The flexibility of Agile allowed the project team to adapt to regulatory changes and integrate user feedback efficiently, significantly enhancing the system’s functionality and user satisfaction.
- Lessons Learned: The primary challenge was confirming compliance with healthcare regulations while maintaining system usability. To stay compliant without compromising functionality, we engaged regulatory experts from the onset and incorporated their feedback throughout the Agile sprints.
3. Software Development: Launching a Mobile App
- Methodology: Scrum
- Results: Achieved a 40% increase in user engagement 20 within the first month of launch.
- Key Highlights: Using Scrum, the team delivered functional app increments every two weeks. This approach kept the team focused and motivated and allowed continuous improvement based on user feedback.
- Lessons Learned: One of the biggest challenges was managing scope creep due to continuous user feedback. The Scrum framework’s emphasis on time-boxed sprints and prioritized backlogs kept the project on track and ensured that essential features were developed first.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid as a Project Manager

Mistake #1: Lack of Clear Goals and Objectives
Starting a project without well-defined goals and objectives might cause uncertainty and mismatched effort.
Quick Solution: Starting with a thorough project charter always guarantees that all stakeholders share the same goal and expected results.
Mistake #2: Poor Communication
Ignoring to maintain open lines of communication leads to misinterpretations and project delays.
Quick Solution: Set frequent meetings and apply cooperative tools to keep everyone updated and involved. Encourage critiques and take quick care of issues.
Mistake #3: Scope Creep
Allowing the project scope to grow unrestrained without appropriate evaluation can throw off budgets and timelines.
Quick Solution: Set a rigid change management system and guarantee that any modifications are completely checked over and approved before they are put into effect.
Mistake #4: Inadequate Risk Management
Failing to recognize and reduce possible risks causes unanticipated problems endangering the project.
Quick Solution: Create backup plans and do a comprehensive risk assessment right through the planning stage.
Mistake #5: Insufficient Resource Allocation
Not allocating enough resources or mishandling them leads to traffic congestion and lower project efficiency.
Quick Solution: To guarantee efficient use of resources, meticulously plan and distribute them; also, routinely check their use.
Mistake #6: Ignoring Stakeholder Engagement
Failing to engage stakeholders during the project lifecycle leads to a lack of support and buy-in.
Quick Solution: Keep stakeholders involved by regular update meetings and ask for their input and feedback.
Advice from Experienced Project Managers
1. “Operations keep the lights on; strategy provides a light at the end of the tunnel, but project management is the train engine that moves the organization forward.” – Joy Gumz, Project management expert and consultant.
2. “Project management is like juggling three balls – time, cost, and quality. Program management is like a troupe of circus performers standing in a circle, each juggling three balls and swapping balls from time to time.” – G. Reiss, author of “Program Management Demystified”
3. “Expect the best, plan for the worst, and prepare to be surprised.” –Denis Waitley, Motivational speaker and author of “The Psychology of Winning.”
4. “Being a Project Manager is like being an artist; you have the different colored process streams combining into a work of art.” – Greg Cimmarrusti, Project management professional and creative thinker.
5. “A good plan can help with risk analysis, but it will never guarantee the smooth running of the project.” –Bentley and Borman, PRINCE2 and Risk Management experts
6. “Get the right people. Then, no matter what else you might do wrong after that, the people will save you. That’s what management is all about.” – Tom DeMarco, author of “Peopleware: Productive Projects and Teams.”
7. “Plans are only good intentions unless they immediately degenerate into hard work.” – Peter Drucker, author of “The Effective Executive.”
Key Terms of Project Management
1. Project Charter: Formally authorizing a project, the project charter comprises the project objectives, scope, stakeholders, and major deliverables and serves as a reference during the project life.
2. Stakeholder: Any person, group, or company capable of influencing or being influenced by the project is a stakeholder. Early involvement stakeholders guarantee their buy-in and support.
3. Scope Creep: The uncontrolled spread of project scope without matching changes to time, cost, or resources is known as “scope creep.” Strict change management techniques control scope creep.
4. Risk Management: The process of identifying, analyzing, and responding to project risks. This involves thorough risk assessments and developing contingency plans.
5. Gantt Chart: A visual tool for project scheduling that shows start and end dates, dependencies, and progress—the Gantt chart is used in visual project management. Tracking chores and schedules depend on Gantt charts.
6. Agile: Agile is a project management method encouraging iterative development, teamwork, and flexibility. Agile techniques including Scrum and Kanban are rather well-known in other sectors including software development.
7. Scrum: Emphasizing iterative development through sprints, frequent feedback loops, and team collaboration, Scrum stresses Scrum lets teams regularly produce functional product increments.
8. Kanban: Kanban, an Agile approach, enhances workflow by means of a visual board for management of work in progress. Its constant delivery method and adaptability are well-known.
9. Waterfall: Following a linear, sequential approach, this classic PM method. Projects with well-defined needs and a clear sequence of stages would benefit most from waterfalls.
10. Critical Path: The series of chores deciding the length of the project. Identiying of the critical path, project managers can guarantee timely completion and effectively distribute resources.
11. PRINCE2: A method for methodically breaking out projects into doable phases of work. Clear roles and responsibilities are stressed in PRINCE2 as is a strong concentration on business justification.
12. Six Sigma: Six Sigma eliminates flaws with a data-driven approach to improving process efficiency and quality. It calls for roles like Black Belts and Green Belts, who oversee efforts at quality control.
13. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): It controls modifications to the resources, schedule, and project scope. Good change management is assessing and approving modifications before they start.
14. Change Management: The process of managing changes to the project scope, schedule, and resources. Effective change management involves evaluating and approving changes before implementation.
15. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Metrics that measure a project’s performance for evaluation. KPIs serve as project management guidelines and point out areas needing work.
Conclusion
- Project management’s principles: Scope, time, cost, quality, risk, and stakeholder management should be your priorities.
- Principal approaches: Know Waterfall’s advantages and uses as well as Agile, Scrum, Kanban, Lean, Six Sigma, and PRINCE2.
- Procedures in Project Management: Move through phases of initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control.
- Roles and competencies: Acknowledge the value of time management, communication, problem-solving, and important roles.
PM practices help you simplify procedures, improve teamwork, and deliver excellent results, whether running a small team or a major project.
Ready to improve your team’s output and share your project management abilities? Start your free trial on Mirorim right now to use the best project management tool that precisely controls your projects and well-being.
Don’t wait; start project management the right way with Mirorim, For FREE!
FAQs | Project Management
Project management is organizing, planning, and supervising a project to reach particular objectives within a given budget and timeframe. To guarantee the project satisfies its intended results, it covers defining project objectives, handling resources, organizing activities, and contacting stakeholders.
Clear Vision and Mission
Comprehensive Planning
Communication
Coordination
Collaboration
Commitment
Continuous Improvement
To honor deadlines in an agile team, use sprint planning to break tasks into manageable parts, maintain regular communication through daily stand-ups, and track progress with burn-down charts. These practices ensure timely delivery by keeping the team aligned and adaptable.
Usually, spending their day organizing and scheduling activities, managing resources, liaising with team members and stakeholders, tracking project development, problem-solving, and planning adjustments as necessary to keep the project on track.
Project manager pay in Canada depends on experience and sector. On average, a project manager makes CAD 75,000 – 110,000 a year, but highly skilled project managers in specialized sectors can make more.
Strong communication and leadership, great problem-solving ability, a thorough awareness of project management techniques, and the capacity to change define a good project manager. They are also quite skilled in properly handling budgets and timeframes.
1. Scope Management
2. Time Management
3. Cost Management
4. Quality Management
5. Resource Management
Assemble Your Team: Ensure everyone understands their roles.
Kickoff Meeting: Start with a meeting to align everyone on goals and expectations.
Follow the Plan: Implement the tasks as outlined in the plan.
Monitor Progress: Regularly track and report on the progress.
Adjust as Needed: Make necessary adjustments to stay on track.
Define the Project
Plan the Project
Assemble the Team
Execute the Plan
Monitor and Control
Close the Project
Project management is the method of organizing, planning, and resource management used to reach particular objectives within a given period. To produce effective project results, the scope, time, money, and quality must all be balanced.
Define Clear Objectives
Plan Thoroughly
Communicate Effectively
Monitor Progress
Adapt and Adjust
Scope
Schedule
Stakeholders
What: The objectives and deliverables.
Why: The purpose and benefits.
Who: The stakeholders and team members.
When: The timeline and milestones.
High responsibility, strict deadlines, and the necessity of continuous coordination and problem-solving define Project Management Office (PMO) roles as demanding ones. Still, good organizational abilities and stress management can help offset this.
A project manager should NOT:
Personally handle all project chores.
Make one-sided choices without reference to stakeholders.
Ignore bottlenecks and problems.
Ignore team spirit and well-being.
Scrum emphasizes the importance of the “daily stand-up” meeting. This quick, daily check-in helps teams stay aligned, identify obstacles, and adjust plans to keep the project on track.
To implement an agile mindset, focus on continuous improvement, prioritize collaboration, deliver value incrementally, and stay adaptable to changes. These tactics help create a responsive and efficient team culture.
Excellent communication and leadership
Problem-Solving
Flexibility and adaptability.
Organizational and time management.
Ability to inspire groups of people.
Usually, in entry-level roles, the lowest-paid project managers make between CAD 50,000 and CAD 60,000 a year, depending on the sector and location.
Bachelor’s degree in business, management, or a closely related field.
Certificates in project management (e.g., PMP, PRINCE2).
Project management experience is invaluable.
Strong leadership and organizing abilities.
The highest-paid project managers work in specialized disciplines, including IT, engineering, and construction. Their salaries range from CAD 120,000 to CAD 150,000 or more, depending on experience and sector.
Extreme Programming (XP) improves project cycle time by aligning work with team capacity. It uses pair programming and test-driven development to ensure efficient, high-quality delivery.
References
- Adegoke, O., Norani, N., & Lucky, E. O. I. (2014). PROJECT MANAGEMENT CHALLENGES AND DIFFICULTIES: A CASE STUDY OF INFORMATION SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266150891_PROJECT_MANAGEMENT_CHALLENGES_AND_DIFFICULTIES_A_CASE_STUDY_OF_INFORMATION_SYSTEM_DEVELOPMENT ↩︎
- The State of Project Management Report 2019. (2019). In Wellingtone. https://wellingtone.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/The-State-of-Project-Management-Report-2019.pdf ↩︎
- Langley, M. A. (2016). The High Cost of Low Performance: How will you improve business results? 8th Global Project Management Survey. Retrieved August 20, 2024, from https://www.pmi.org/-/media/pmi/documents/public/pdf/learning/thought-leadership/pulse/pulse-of-the-profession-2016 ↩︎
- Langley, M. A. (2016). The High Cost of Low Performance: How will you improve business results? 8th Global Project Management Survey. Retrieved August 20, 2024, from https://www.pmi.org/-/media/pmi/documents/public/pdf/learning/thought-leadership/pulse/pulse-of-the-profession-2016 ↩︎
- Langley, M. A. (2016). The High Cost of Low Performance: How will you improve business results? 8th Global Project Management Survey. Retrieved August 20, 2024, from https://www.pmi.org/-/media/pmi/documents/public/pdf/learning/thought-leadership/pulse/pulse-of-the-profession-2016 ↩︎
- Project Management Institute (2021). Beyond Agility: Flex to the Future. Pulse of the Profession. https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/beyond-agility-gymnastic-enterprises-12973 ↩︎
- Harris, K. (2023, October 4). Agile vs Waterfall – Which method works best? Igale. https://igale.co.uk/insights/agile-waterfall-method-works-best/ ↩︎
- The 10th annual State of AgileTM survey. (2015). In VersionOne. https://www.devops.ch/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/VersionOne-10th-Annual-State-of-Agile-Report.pdf ↩︎
- Rooney, P. (2017). Agile Project Delivery. https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/actuarial-insurance-services/assets/agile-project-delivery-confidence.pdf ↩︎
- Chong, E., Handscomb, C., Maj, T., & Markenday, R. (2022, October 24). In pursuit of value—not work. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/people-and-organizational-performance/our-insights/in-pursuit-of-value-not-work ↩︎
- Toyota Production System – Lean Enterprise Institute. (2020, July 2). Lean Enterprise Institute. https://www.lean.org/lexicon-terms/toyota-production-system/ ↩︎
- Espel, P., Herbener, M., Rupprecht, F., Schröpfer, C., & Venus, A. (2020, April 17). How industrial companies can cut their indirect costs—fast. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/automotive-and-assembly/our-insights/how-industrial-companies-can-cut-their-indirect-costs-fast ↩︎
- How continuous improvement can build a competitive edge. (2019, May 6). McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/people-and-organizational-performance/our-insights/the-organization-blog/how-continuous-improvement-can-build-a-competitive-edge ↩︎
- The impact of agility: How to shape your organization to compete. (2021, May 25). McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/people-and-organizational-performance/our-insights/the-impact-of-agility-how-to-shape-your-organization-to-compete ↩︎
- Smrakibb. (2023, December 1). Unveiling the Success of Six Sigma: A Case Study – Lean Six Sigma Bureau. Lean Six Sigma Training. https://leansixsigmabureau.com/en-us/unveiling-the-success-of-six-sigma-a-case-study/ ↩︎
- Jordan, E., Kušar, J., Rihar, L., & Berlec, T. (2019). Portfolio analysis of a Lean Six Sigma production process. Central European Journal of Operations Research, 27(3), 797–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10100-019-00613-4 ↩︎
- Maximising productivity with Lean Six Sigma. (2020). https://assets.kpmg.com/content/dam/kpmg/in/pdf/2020/04/Maximising-Productivity-with-Lean-Six-Sigma.pdf ↩︎
- Muscolino, H. (2017). Transforming Business Workflows with Enterprise Information Capture. https://www.alarisworld.com/-/media/static-picturepark-assets/impublicwebsite/insights/idc-analyst-connection-q2-2017.pdf ↩︎
- Meghna Desai, Miriam Tardif-Douglin, Indigo R. D. Miller, Stephanie C. Blitzer, David L. Gardner, Teresa M. Thompson, LaPonda Edmondson, David M. Levine
medRxiv 2023.12.12.23299864; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.12.12.23299864 ↩︎ - McDonald, K. (2023, March 18). Using Agile in Clinical Decision Support Development | Agile Alliance. Agile Alliance |. https://www.agilealliance.org/resources/experience-reports/agile-clinical-decision-support-developments/ ↩︎

